Unit 11 homework 4 area of regular figures answers – Embark on a journey to master the intricacies of area calculations for regular figures with Unit 11 Homework 4: Area of Regular Figures Answers. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts, formulas, and applications of area, empowering you to navigate the world of geometry with confidence and precision.
Prepare to uncover the secrets of regular polygons, their defining properties, and the ingenious formulas that unlock their areas. Discover how these formulas are applied in real-world scenarios, from architecture to land surveying, and gain invaluable problem-solving skills through a series of carefully crafted practice problems.
1. Introduction to Area of Regular Figures
Area is a fundamental concept in geometry that measures the amount of two-dimensional space occupied by a figure. It plays a vital role in various fields, including architecture, construction, and land surveying.
Regular polygons are two-dimensional shapes with equal side lengths and equal interior angles. Examples of regular polygons include squares, triangles, and hexagons.
2. Formulas for Calculating Area
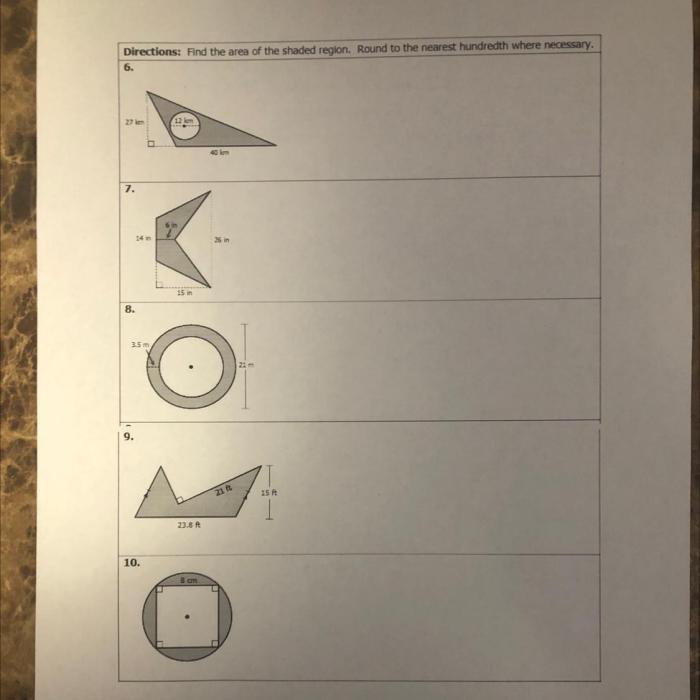
| Polygon Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Square | Area = side length2 | If a square has a side length of 5 cm, its area is 25 cm2. |
| Rectangle | Area = length × width | If a rectangle has a length of 6 cm and a width of 4 cm, its area is 24 cm2. |
| Triangle | Area = (1/2) × base × height | If a triangle has a base of 8 cm and a height of 6 cm, its area is 24 cm2. |
| Parallelogram | Area = base × height | If a parallelogram has a base of 10 cm and a height of 5 cm, its area is 50 cm2. |
| Trapezoid | Area = (1/2) × (base1 + base2) × height | If a trapezoid has bases of 8 cm and 12 cm, and a height of 6 cm, its area is 60 cm2. |
3. Applications of Area Calculations
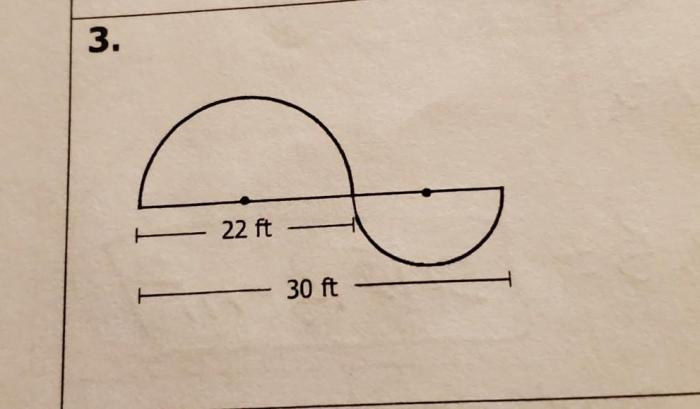
Area calculations have numerous practical applications in real-life scenarios:
- Architecture and Construction:Determining the area of a building’s floor plan helps architects and builders estimate materials needed and optimize space utilization.
- Land Surveying:Surveyors use area calculations to determine the size and boundaries of land parcels for legal and planning purposes.
- Agriculture:Farmers calculate the area of their fields to determine crop yield and fertilizer requirements.
4. Problem-Solving with Area
Problem 1:Calculate the area of a square with a side length of 7 cm.
Solution:Area = side length 2= 7 2= 49 cm 2.
Problem 2:Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 10 cm and a width of 6 cm.
Solution:Area = length × width = 10 × 6 = 60 cm 2.
5. Extensions and Advanced Concepts
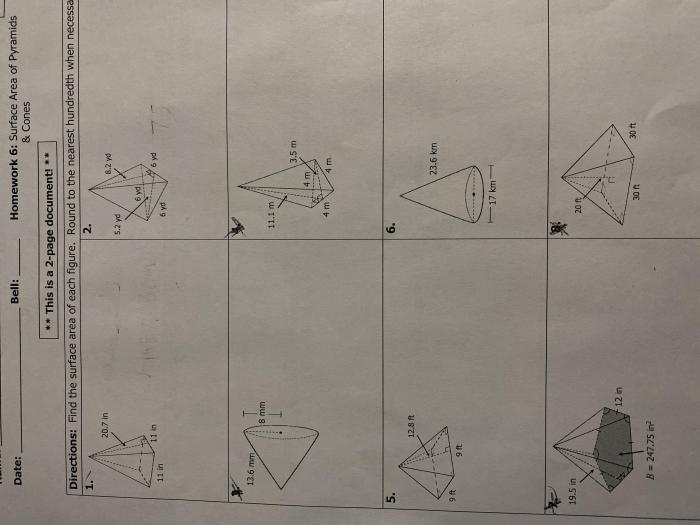
Composite Figures:Area calculations can be extended to composite figures, which are shapes made up of two or more regular figures.
Perimeter:Perimeter is the distance around the boundary of a figure. It is related to area through the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
FAQ Compilation: Unit 11 Homework 4 Area Of Regular Figures Answers
What is the formula for calculating the area of a square?
A = s^2, where s is the length of a side.
How can I find the area of a trapezoid?
A = (b1 + b2) – h / 2, where b1 and b2 are the lengths of the parallel bases and h is the height.
What are the applications of area calculations in real life?
Area calculations are used in architecture, construction, land surveying, and many other fields to determine materials needed, optimize space utilization, and solve practical problems.
