Blizzards and hurricanes are examples of contrasting observable events. – Blizzards and hurricanes are examples of contrasting observable events, showcasing the diverse forces of nature. These weather phenomena exhibit distinct characteristics, formation processes, and societal impacts, providing valuable insights into the complexities of our planet’s atmospheric systems.
Blizzards, characterized by blinding snow and fierce winds, form in frigid environments. Hurricanes, on the other hand, are tropical cyclones that unleash torrential rains and destructive winds. Their geographical distribution and seasonal occurrences further highlight their contrasting nature.
Blizzards

Blizzards are severe snowstorms characterized by strong winds, low visibility, and significant snowfall. They typically occur in high-latitude regions during winter months.
Causes and Formation
Blizzards form when a cold front meets a warm front, causing the warm air to rise rapidly and the cold air to descend. As the cold air descends, it picks up moisture from the ground and forms clouds. The clouds then release the moisture as snow, which is blown by the strong winds.
Characteristics and Effects
- Snowfall rates of more than 5 centimeters per hour
- Wind speeds of at least 56 kilometers per hour
- Visibility of less than 400 meters
Blizzards can have severe impacts on human populations and infrastructure. They can cause power outages, transportation delays, and property damage. In extreme cases, blizzards can be deadly.
Notable Blizzards
- The Great Blizzard of 1888, which affected the eastern United States and killed hundreds of people
- The Blizzard of 1978, which paralyzed the northeastern United States and caused billions of dollars in damage
- The Blizzard of 2010, which affected the mid-Atlantic and northeastern United States and caused widespread power outages
- Wind speeds of at least 119 kilometers per hour
- Heavy rainfall, which can lead to flooding
- Storm surges, which are walls of water that can reach heights of several meters
- Hurricane Katrina, which devastated the Gulf Coast of the United States in 2005
- Hurricane Sandy, which affected the northeastern United States in 2012
- Hurricane Maria, which devastated Puerto Rico and other Caribbean islands in 2017
- Developing evacuation plans
- Stockpiling food and water
- Securing loose objects
- Listening to weather forecasts
- Following the instructions of local authorities
Hurricanes
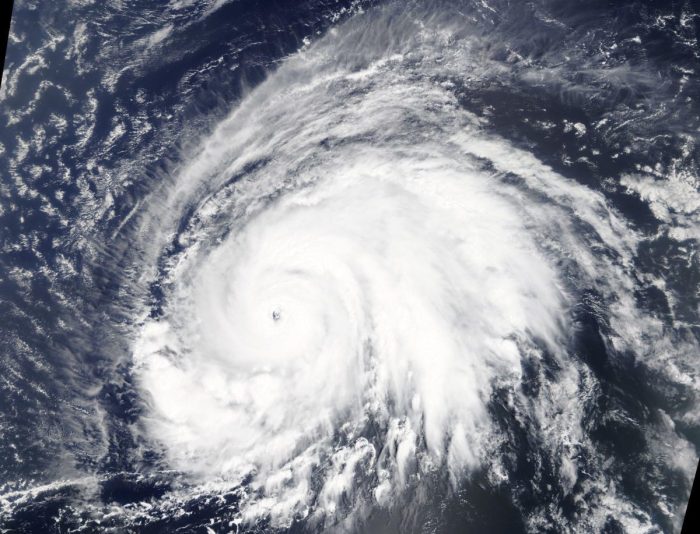

Hurricanes are intense tropical cyclones that form over warm ocean waters. They are characterized by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
Causes and Formation
Hurricanes form when warm, moist air rises from the ocean surface and condenses into clouds. The clouds then rotate and form a low-pressure system. As the low-pressure system intensifies, the winds become stronger and the storm develops a central eye.
Characteristics and Effects
Hurricanes can have devastating impacts on human populations and infrastructure. They can cause widespread destruction, power outages, and loss of life.
Notable Hurricanes, Blizzards and hurricanes are examples of contrasting observable events.
Contrasting Characteristics: Blizzards And Hurricanes Are Examples Of Contrasting Observable Events.

Blizzards and hurricanes are two very different types of storms. They occur in different geographical locations, seasons, and have different scales and intensities.
Geographical Locations and Seasons
Blizzards occur in high-latitude regions during winter months. Hurricanes, on the other hand, occur in tropical and subtropical regions during the summer and fall months.
Scales and Intensities
Blizzards are typically smaller in scale than hurricanes. They can cover an area of a few hundred kilometers, while hurricanes can cover an area of thousands of kilometers. Hurricanes are also more intense than blizzards. They have higher wind speeds and can produce more rainfall.
Impact on Society
Blizzards and hurricanes can have a significant impact on human populations, infrastructure, and the environment.
Human Populations
Blizzards and hurricanes can cause injuries and death. They can also damage homes and businesses, and disrupt transportation and communication. In extreme cases, blizzards and hurricanes can force people to evacuate their homes.
Infrastructure
Blizzards and hurricanes can damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. They can also cause power outages and water shortages.
Environment
Blizzards and hurricanes can damage forests and other ecosystems. They can also lead to erosion and flooding.
Preparation and Response
There are a number of things that can be done to prepare for and respond to blizzards and hurricanes. These include:
Role of Technology and Forecasting
Technology and forecasting play an important role in mitigating the impacts of blizzards and hurricanes. Weather forecasting can help people to prepare for storms and to avoid dangerous areas. Technology can also be used to track storms and to provide real-time updates on their progress.
FAQ
What are the key differences between blizzards and hurricanes?
Blizzards occur in cold climates and are characterized by heavy snowfall, low visibility, and strong winds. Hurricanes, on the other hand, form over warm ocean waters and bring intense rainfall, high winds, and storm surges.
How do blizzards and hurricanes impact society?
Blizzards can disrupt transportation, cause power outages, and lead to hypothermia and frostbite. Hurricanes can cause widespread flooding, property damage, and loss of life due to high winds and storm surges.